Research Laboratory

Leadership
Jerome Siegel, PhD
Director
Contact Info
Sleep Research Website
Neurobiology Research 151A3
VAGLAHS, North Hills, CA
jsiegel@ucla.edu
1-818-891-8612
About
We have been focused on determining the function of sleep, the cause of narcolepsy and the function of the peptide hypocretin (Hcrt or orexin).
We were the first to report the loss of hypothalamic hypocretin neurons in human narcolepsy (in 2000, see below-left, submitted to Society for Neuroscience meeting March 5, 2000 and [PMID:11055430], the first to record hypocretin neurons in behaving animals (in 2005 [PMID:15924864], finding that these neurons fired in relation to approach/pleasurable behavior (click here to see video) and the first to record Hcrt release in the human brain (in 2013 [PMID:23462990]), finding greatly elevated Hcrt release during pleasurable social interactions and minimal release during aversion, disappointment or pain. Neither the activity of Hcrt neurons in rats, nor Hcrt release in humans are strongly correlated with EEG activation or with muscle tone, the two parameters that are altered in narcolepsy. The loss of hypocretin neurons may be responsible for the increased incidence of depression in people with narcolepsy, but the major symptoms of narcolepsy cannot be explained by the loss of these neurons.
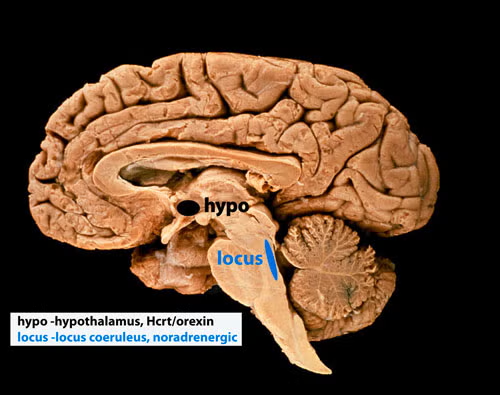
Five to thirty percent of people having narcolepsy with cataplexy have absolutely normal levels of hypocretin in their cerebrospinal fluid [PMID: 10615891]; [PMID: 12374492]; [PMID: 17702265]; [PMID 33539807]; [PMID: 30679597]; [PMID: 26564387]; [PMID: 32406370]; [PMID: 22942503]; [PMID 16006155], findings that do not support the hypothesis that hypocretin loss causes sleepiness and cataplexy, the major symptoms of narcolepsy. In 2025 we discovered that all humans with narcolepsy also have a loss of locus coeruleus noradrenergic neurons (Chi squared p=0.001), comparable in magnitude to their loss of hypocretin neurons [doi.org/10.1101/2025.04.12.648456]. Locus coeruleus neurons facilitate muscle tone and their discharge cessation is correlated with the muscle tone suppression of REM sleep [PMID:10391445]. Thus their loss can explain cataplexy [doi.org/10.1101/2025.04.12.648456]. These noradrenergic neurons also have ascending axons and their loss decreases alertness [PMID:11549748], [PMID:20668280]). Our recent study [doi.org/10.1101/2025.04.12.648456] shows that the loss of locus coeruleus neurons is not caused by the loss of hypocretin neurons.
The two neuronal losses, of hypocretin neurons in the forebrain and of norepinephrine neurons in the brainstem locus coeruleus (see photo below), may be caused simultaneously or sequentially by an autoimmune process [PMID:3010426]. About 150,000 Americans have narcolepsy, a lifelong disorder.
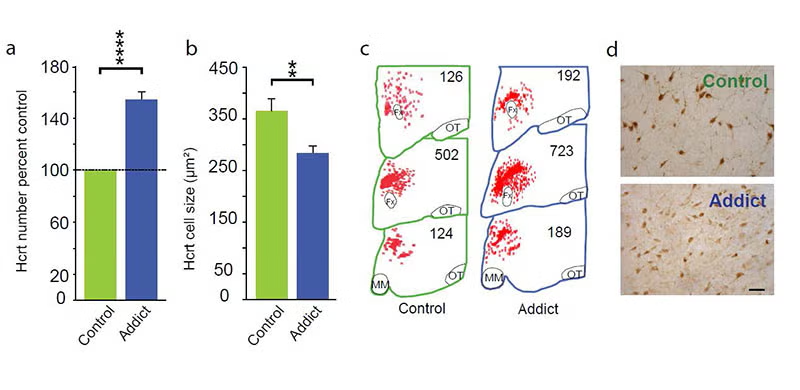
In 2018, 2024 and 2025 (below-left column) we discovered that hypocretin neurons have a major role in opioid addiction. Chronic use of heroin in humans and daily injection of morphine in mice increases the number of detected hypocretin neurons and decreases their size (see figure below). We find that opioid dependence is prevented in mice by deleting hypocretin neurons. In 2024 we found that opioid dependence is prevented, without reducing opioid analgesia, by blocking hypocretin receptors with suvorexant when administering opioids [PMID: 39989723]. About 8 million Americans are dependent on opioids. Opioid dependence caused more than 55,000 opioid overdose deaths last year in the United States. Most individuals who die from an opioid overdose, had their first exposure to opioids prescribed for analgesia.
Bibliography: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/myncbi/jerome.siegel.1/bibliography/public/
About the Center for Sleep Research
We study the control and disorders of REM sleep. We also study sleep in animals to identify the evolutionary determinants and functions of sleep.
Work in this laboratory is supported by the National Institutes of Health, the National Science Foundation and the Department of Veterans Affairs.
A major focus of the laboratory is understanding the hypocretin/orexin system and its role in opioid addiction and narcolepsy, in work supported by NIDA (National Institute on Drug Abuse).
Director: Jerome M. Siegel
UCLA (University of California, Los Angeles), Department of Psychiatry,
Neurobiology Research, VA GLAHS (Greater Los Angeles Healthcare System),
North Hills, California 91343,
U.S.A.
Bibliography: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/myncbi/jerome.siegel.1/bibliography/public/
Professional Positions
| 1984-present | Professor of Psychiatry and Biobehavioral Sciences, Member Brain Research Institute, UCLA School of Medicine |
| 1993-1999 | Chair, Program Committee, APSS (Association of Professional Sleep Societies) |
| 1984-1989 | Associate Professor of Psychiatry & Biobehavioral Sciences, UCLA, School of Medicine |
| 1980-present | Chief, Neurobiology Research, Sepulveda VAMC (Veterans Affairs Medical Center) |
| 1978-1984 | Assistant Professor of Psychiatry & Biobehavioral Sciences, UCLA, School of Medicine |
Awards and Other Professional Activities
| 2013 | Narcolepsy Researcher of the Year, The Narcolepsy Network (the main US patient group) |
| 2011 | William S. Middleton Award; for Outstanding Achievement in Biomedical Research, (the national award of the VA for research excellence) |
| 1999-2006 | Jacob Javits Neuroscience Investigator Award, NINDS (National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke) |
| 2005 | Dement Award, American Academy of Sleep Medicine, for clinical research |
| 1994-2004 | M.E.R.I.T. Award, NHLBI (National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute) |
| 2002 | Distinguished Scientist Award, Sleep Research Society |
| 2001 | Special Award for Research Leading to the Discovery of the Cause of Human Narcolepsy, Sleep Research Society |
| 1992-1995 | President-Elect, President, Past-President Sleep Research Society |
| 1980 | V.A. Clinical Investigator Award |
Overview of common sleep disorders
Sleep disorders affect more than 10% of the population. Effective treatments are available for some, whereas the cause and cure for others remain unknown.
- Sleep apnea. This periodic interruption of breathing, characterized by loud, interrupted snoring, affects more than 5% of adult males and can shorten lifespan more than smoking a pack of cigarettes a day. You can listen to an example of sleep apnea.
Sleep apnea is caused by the excessive relaxation of airway muscles during sleep. It can be effectively treated by wearing a mask that pressurizes the airway, a procedure called CPAP, or continuous positive airway pressure. In mild cases, weight loss and preventing sufferers from sleeping on their backs can help. - Insomnia. This is even more common than sleep apnea. Sleeping pills can be helpful for short-term insomnia, but may not produce a longerm improvement, and may even have significant adverse effects, including shortening lifespan, when used frequently. Insomnia is more common later in life. The cause of this increase is unclear.
- Restless legs, PLM. One syndrome that is known to produce a profound insomnia is “restless legs with periodic movements during sleep.” “Restless legs” refers to an urge to move the legs that increases during quiescence. Periodic movement during sleep, a frequent accompaniment of restless legs, is a regular twitching, usually occurring every 5-90 seconds, usually in the legs, during nonREM sleep and can also disturb sleep. Periodic movement during sleep is present in as much as 10% of the adult population. Iron deficiency is a correlate and dopaminergic drugs can be effective in reducing symptoms
- Parasomnias. Night terrors, in which children scream during the night, sleep walking and bedwetting are some of the most common and are generally outgrown with age. Parasomnias include bruxism, a grinding of the teeth that can be treated by wearing a dental device.
- REM sleep behavior disorder. This disorder is characterized by vigorous movements occurring during REM sleep as the dreamer acts out his or her dream. The patient and those sharing the bed can be injured. Effective drug treatments, often using the benzodiazepine clonazepam, are available. REM behavior disorder often leads to Parkinson’s disease.
- Narcolepsy. This disorder is characterized by excessive daytime sleepiness and by sudden losses of muscle tone in waking called cataplexy. In 2025, we found an extensive loss of noradrenergic neruons in the locus coeruleus, neurons we had previously identified as linked to the loss of muscle tone in cataplexy.
The non-profit American Academy of Sleep Medicine 630-737-0700 has a list of accredited sleep disorders treatment centers www.sleepeducation.com/find-a-center.
Publications
2025
T.C. Thannickal; M.F. Wu; M.E. Cornford; J.M. Siegel “Brainstem pathology in human narcolepsy: Neurodegeneration in the locus coeruleus in all narcoleptic humans, but not in genetically narcoleptic mice or dogs” [Full Text]
Paper shows that narcolepsy is not simply caused by “loss of hypocretin/orexin”.
E.A. Berry; E.M. Huhulea; M. Ishibashi; R. McGregor; J.M. Siegel; C.S. Leonard “Chronic but not acute morphine exposure reversibly impairs spike generation and repetitive firing in a functionally distinct subpopulation of orexin neurons” [Full Text]
I.B. Malungo; A. Ngwenya; M.F. Bertelsen; M. Spocter; T.C. Thannickal; J.M. Siegel; P.R. Manger “The complexly parcellated, yet quantitatively reduced, orexinergic/ hypocretinergic system of humans” [Full Text]
2024
R. McGregor; M.F. Wu; T.C. Thannickal; S. Li; J.M. Siegel “Opioid-induced neuroanatomical, microglial and behavioral changes are blocked by suvorexant without diminishing opioid analgesia” [Full Text], [Full Text]
M.J. Thorpy; J.M. Siegel; Y. Dauvilliers “REM sleep in narcolepsy” [Full Text]
O.I. Lyamin; “Sleep: Giving it up to get it on” [Full Text]
2023
M.F. Wu; T. Thannickal; S. Li; R. McGregor; J.M. Siegel “Effects of sodium oxybate on hypocretin/orexin and locus coeruleus neurons” [Full Text]
G. Aston-Jones; P. Bonaventure; P. Coleman; L. de Lecea; D. Hartman; D. Hoyer; L. Jacobson; T. Kilduff; J.P. Kukkonen; T.P. McDonald; R. Porter; J. Renger; T. Sakurai; J.M. Siegel; G. Sutcliffe; N. Upton; C.J. Winrow; MasashiYanagisawa “IUPHAR/BPS Guide to Pharmacology CITEhttps://doi.org/10.2218/gtopdb/F51/2023.1 Orexin receptors in GtoPdb v.2023.1” [Full Text]
J.M. Siegel “REM sleep function: mythology vs. reality” [Full Text]
R. McGregor; A. Matzeu; T. Thannickal; F. Wu; M. Cornford; R. Martin-Fardon; J.M. Siegel “Sensitivity of hypocretin system to chronic alcohol exposure: a human and animal study” [Full Text]
2022
A.V. Salminen; S. Clemens; D. García-Borreguero; I. Ghorayeb; Y. Li; M. Manconi; W. Ondo; D. Rye; J.M. Siegel; A. Silvani; J.W. Winkelman; R.P. Allen; S. Ferré “Consensus guidelines on the construct validity of rodent models of restless legs syndrome.”
J.M. Siegel “Defining sleep” [Full Text]
J.M. Siegel “Evolution of mammalian sleep” [Full Text]
R. McGregor; M.F. Wu; B. Holmes; H.Anh Lam; N.T. Maidment; J. Gera; A. Yamanaka; J.M. Siegel “Hypocretin/orexin interactions with norepinephrine contribute to the opiate withdrawal syndrome.” [Full Text]
J.M. Siegel “Rapid eye movement sleep control and function” [Full Text]
J.M. Siegel “Sleep function: an evolutionary perspective.” [Full Text]
J.M. Siegel “Sleep in mammals” [Full Text]
Y.Y. Lai; K.C. Hsieh; K.T. Chew; D. Nguyen; J.M. Siegel “Striatal mechanism of the restless legs syndrome” [Full Text]
2021
J.M. Siegel “Memory consolidation Is similar in waking and sleep” [Full Text]
V.M. Williams; A. Bhagwandin; J. Swiegers; M.F. Bertelsen; T. Hård; T.C. Thannickal; J.M. Siegel; C.C. Sherwood; P.R. Manger “Nuclear organization of orexinergic neurons in the hypothalamus of a lar gibbon and a chimpanzee” [Full Text]
P. Coleman; L. de Lecea; A. Gotter; J. Hagen; D. Hoyer; T. Kilduff; J.P. Kukkonen; R. Porter; J. Renger; J.M. Siegel; G. Sutcliffe; N. Upton; C.J. Winrow “Orexin receptors in GtoPdb v.2021.3” [Full Text]
R. McGregor; T. Thannickal; J.M. Siegel “Pleasure, addiction and hypocretin (orexin)” [Full Text]
O.I. Lyamin; J.M. Siegel; E.A. Nazarenko; V.V. Rozhnov “Sleep in the lesser mouse-deer (Tragulus kanchil)” [Full Text], [Full Text]
2020
A.V. Salminen; A. Silvani; R.P. Allen; S. Clemens; D. Garcia‐Borreguero; I. Ghorayeb; S. Ferré; Y. Li; W. Ondo; D.L. Picchietti; D. Rye; J.M. Siegel; J.W. Winkelman; M. Manconi “Consensus Guidelines on Rodent Models of Restless Legs Syndrome” [Full Text]
P.R. Manger; J.M. Siegel “Do all mammals dream?” [Full Text]
A. Kostin; M.Aftab Alam; J.M. Siegel; D. McGinty; M.Noor Alam “Sex- and age-dependent differences in sleep-wake characteristics of fisher-344 rats.” [Full Text]
O.I. Lyamin; A.S. Kibalnikov; J.M. Siegel “Sleep in ostrich chicks (Struthio camelus)” [Full Text], [Full Text]
J.M. Siegel “Sleep under evolutionarily relevant conditions.” [Full Text]
Y.Y. Lai; K.C. Hsieh; Y.H. Cheng; K.T. Chew; D. Nguyen; L. Ramanathan; J.M. Siegel “Striatal histamine mechanism in the pathogenesis of restless legs syndrome.” [Full Text]
Y.Y. Lai; T. Kodama; K.C. Hsieh; D. Nguyen; J.M. Siegel “Substantia nigra pars reticulata-mediated sleep and motor activity regulation” [Full Text]
2019
J.M. Kendall-Bar; A.L. Vyssotski; L.M. Mukhametov; J.M. Siegel; O.I. Lyamin “Eye state asymmetry during aquatic unihemispheric slow wave sleep in northern fur seals (Callorhinus ursinus).” [Full Text]
O.I. Lyamin; J.M. Siegel “Sleep in aquatic mammals” [Full Text]
A.N. Smit; T. Broesch; J.M. Siegel; R.E. Mistlberger “Sleep timing and duration in indigenous villages with and without electric lighting on Tanna Island, Vanuatu.” [Full Text]
2018
M.Aftab Alam; A. Kostin; J. Siegel; D. McGinty; R. Szymusiak; M.Noor Alam “Characteristics of Sleep-Active Neurons in the Medullary Parafacial Zone in Rats.” [Full Text]
O.I. Lyamin; P.O. Kosenko; S.M. Korneva; A.L. Vyssotski; L.M. Mukhametov; J.M. Siegel “Fur seals suppress REM sleep for very long periods without subsequent rebound.” [Full Text], [Full Text], [Full Text], [Full Text]
T.C. Thannickal; J. John; L. Shan; D.F. Swaab; M.F. Wu; L. Ramanathan; R. McGregor; K.T. Chew; M. Cornford; A. Yamanaka; A. Inutsuka; R. Fronczek; G.Jan Lammers; P.F. Worley; J.M. Siegel “Opiates increase the number of hypocretin-producing cells in human and mouse brain and reverse cataplexy in a mouse model of narcolepsy.” [Full Text], [Full Text], [Full Text], [Full Text]
J.M. Siegel “Sleep phylogenetic evolution and ontogeny, Avidan Ed.” [Full Text]
C.E.H.M. Donjacour; G.Jan Lammers; J.M. Siegel “Striking cessation of cataplexy by opioids.” [Full Text]
S.P. Prall; G. Yetish; B.A. Scelza; J.M. Siegel “The influence of age- and sex-specific labor demands on sleep in Namibian agropastoralists.” [Full Text]
2017
R. McGregor; L. Shan; M.F. Wu; J.M. Siegel “Diurnal fluctuation in the number of hypocretin/orexin and histamine producing: Implication for understanding and treating neuronal loss” BibTex [Full Text], [Full Text]
N. Gravett; A. Bhagwandin; R. Sutcliffe; K. Landen; M.J. Chase; O.I. Lyamin; J.M. Siegel; P.R. Manger “Inactivity/sleep in two wild free-roaming African elephant matriarchs – Does large body size make elephants the shortest mammalian sleepers?” [Full Text]
Y.Y. Lai; Y.H. Cheng; K.C. Hsieh; D. Nguyen; K.T. Chew; L. Ramanathan; J.M. Siegel “Motor hyperactivity of the iron-deficient rat – an animal model of restless legs syndrome.” BibTex [Full Text]
“Rapid eye movement sleep” BibTex [Full Text]
“Sleep in animals: a state of adaptive inactivity” [Full Text]
O.I. Lyamin; L.M. Mukhametov; J.M. Siegel “Sleep in the northern fur seal.” [Full Text]
2016
O.I. Lyamin; J.L. Lapierre; P.O. Kosenko; T. Kodama; A. Bhagwandin; S.M. Korneva; J.H. Peever; L.M. Mukhametov; J.M. Siegel “Monoamine release during unihemispheric sleep and unihemispheric waking in the fur seal.” BibTex [Full Text], [Full Text], [Full Text]
P.M. Macey; M.K. Sarma; R. Nagarajan; R. Aysola; J.M. Siegel; R.M. Harper; A. Thomas “Obstructive sleep apnea is associated with low GABA and high glutamate in the insular cortex” [Full Text]
L.A. Dell; N. Patzke; M.A. Spocter; J.M. Siegel; P.R. Manger “Organization of the sleep-related neural systems in the brain of the harbour porpoise (Phocoena phocoena).” [Full Text]
L.A. Dell; K.Ae Karlsson; N. Patzke; M.A. Spocter; J.M. Siegel; P.R. Manger “Organization of the sleep-related neural systems in the brain of the minke whale (Balaenoptera acutorostrata).” [Full Text]
L.A. Dell; N. Patzke; M.A. Spocter; M.F. Bertelsen; J.M. Siegel; P.R. Manger “Organization of the sleep-related neural systems in the brain of the river hippopotamus (Hippopotamus amphibius): A most unusual cetartiodactyl species.” BibTex [Full Text]
2015
R. McGregor; J.M. Siegel “Control of sleep in mammals (poster)” [Full Text], [Full Text], [Full Text], [Full Text]
O.I. Lyamin; S.M. Korneva; E.D. Obukhova; L.M. Mukhametov; J.M. Siegel “Evaluation of the ability of northern fur seals to perceive and visually discriminate images under the conditions of sleep loss.” [Full Text]
T.C. Thannickal; J.M. Siegel “Hypocretin/Orexin Pathology in Human Narcolepsy with and Without Cataplexy” [Full Text]
N. Patzke; M.A. Spocter; K.Æ. Karlsson; M.F. Bertelsen; M. Haagensen; R. Chawana; S. Streicher; C. Kaswera; E. Gilissen; A.N. Alagaili; O.B. Mohammed; R.L. Reep; N.C. Bennett; J.M. Siegel; A.O. Ihunwo; P.R. Manger “In contrast to many other mammals, cetaceans have relatively small hippocampi that appear to lack adult neurogenesis.” [Full Text]
L. Shan; Y. Dauvilliers; J.M. Siegel “Interactions of the histamine and hypocretin systems in CNS disorders.” BibTex [Full Text]
G. Yetish; H. Kaplan; M. Gurven; B. Wood; H. Pontzer; P.R. Manger; C. Wilson; R. McGregor; J.M. Siegel “Natural sleep and its seasonal variations in three pre-industrial societies.” [Full Text], [Full Text], [Full Text], [Full Text], [Full Text]
L.A. Dell; M.A. Spocter; N. Patzke; K.Æ. Karlson; A.N. Alagaili; N.C. Bennett; O.B. Muhammed; M.F. Bertelsen; J.M. Siegel; P.R. Manger “Orexinergic bouton density is lower in the cerebral cortex of cetaceans compared to artiodactyls.” [Full Text]
2014
Y. Dauvilliers; J.M. Siegel; R. Lopez; Z.A. Torontali; J.H. Peever “Cataplexy–clinical aspects, pathophysiology and management strategy.” [Full Text]
L. Ramanathan; J.M. Siegel “Gender differences between hypocretin/orexin knockout and wild type mice: age, body weight, body composition, metabolic markers, leptin and insulin resistance.” [Full Text]
A. Kostin; J.M. Siegel; M.Noor Alam “Lack of hypocretin attenuates behavioral changes produced by glutamatergic activation of the perifornical-lateral hypothalamic area.” [Full Text]
2013
J. John; T.C. Thannickal; R. McGregor; L. Ramanathan; H. Ohtsu; S. Nishino; N. Sakai; A. Yamanaka; C. Stone; M. Cornford; J.M. Siegel “Greatly increased numbers of histamine cells in human narcolepsy with cataplexy.” [Full Text] [Full Text]
A.M. Blouin; I. Fried; C.L. Wilson; R.J. Staba; E.J. Behnke; H.A. Lam; N.T. Maidment; K.Æ. Karlsson; J.L. Lapierre; J.M. Siegel “Human hypocretin and melanin-concentrating hormone levels are linked to emotion and social interaction.” [Full Text]
K.C. Hsieh; D. Nguyen; J.M. Siegel; Y.Y. Lai “New pathways and data on rapid eye movement sleep behaviour disorder in a rat model.” [Full Text]
C.H. Schenck; J.Y. Montplaisir; B. Frauscher; B. Hogl; J.F. Gagnon; R. Postuma; K. Sonka; P. Jennum; M. Partinen; I. Arnulf; C. de Cock; Y. Dauvilliers; P.H. Luppi; A. Heidbreder; G. Mayer; F. Sixel-Döring; C. Trenkwalder; M. Unger; P. Young; Y.K. Wing; L. Ferini-Strambi; R. Ferri; G. Plazzi; M. Zucconi; Y. Inoue; A. Iranzo; J. Santamaria; C. Bassetti; J.C. Möller; B.F. Boeve; Y.Y. Lai; M. Pavlova; C. Saper; P. Schmidt; J.M. Siegel; C. Singer; E. St Louis; A. Videnovic; W. Oertel “Rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder: devising controlled active treatment studies for symptomatic and neuroprotective therapy–a consensus statement from the International Rapid Eye Movement Sleep Behavior Disorder Study Group.” [Full Text]
A.M. Blouin; J.M. Siegel “Relation of melanin concentrating hormone levels to sleep, emotion and hypocretin levels.” [Full Text]
“REM sleep anatomy and physiology” [Full Text]
“Sleep in Aquatic Species” [Full Text]
J.L. Lapierre; P.O. Kosenko; T. Kodama; J.H. Peever; L.M. Mukhametov; O.I. Lyamin; J.M. Siegel “Symmetrical serotonin release during asymmetrical slow-wave sleep: implications for the neurochemistry of sleep-waking states.” [Full Text]
J. Siegel “The evolution of sleep” [Full Text]
2012
T.E. Scammell; J.K. Matheson; M. Honda; T.C. Thannickal; J.M. Siegel “Coexistence of narcolepsy and Alzheimer’s disease.” [Full Text], [Full Text]
J.M. Siegel “Evolution. Suppression of sleep for mating.” [Full Text]
K.C. Hsieh; D. Nguyen; J.M. Siegel; Y.Y. Lai “New pathways and data on REM sleep behaviour disorder in a rat model.” [Full Text]
L.A. Dell; N. Patzke; A. Bhagwandin; F. Bux; K. Fuxe; G. Barber; J.M. Siegel; P.R. Manger “Organization and number of orexinergic neurons in the hypothalamus of two species of Cetartiodactyla: a comparison of giraffe (Giraffa camelopardalis) and harbour porpoise (Phocoena phocoena).” [Full Text]
O.I. Lyamin; I.F. Pavlova; P.O. Kosenko; L.M. Mukhametov; J.M. Siegel “Regional differences in cortical electroencephalogram (EEG) slow wave activity and interhemispheric EEG asymmetry in the fur seal.” [Full Text]
N. Gravett; A. Bhagwandin; O.I. Lyamin; J.M. Siegel; P.R. Manger “Sleep in the rock hyrax, Procavia capensis.” [Full Text]
O.I. Lyamin; P.O. Kosenko; A.L. Vyssotski; J.L. Lapierre; J.M. Siegel; L.M. Mukhametov “Study of sleep in a walrus.” [Full Text], [Full Text]
2011
M.F. Wu; R. Nienhuis; N. Maidment; H.A. Lam; J.M. Siegel “Cerebrospinal fluid hypocretin (orexin) levels are elevated by play but are not raised by exercise and its associated heart rate, blood pressure, respiration or body temperature changes.” [Full Text]
R. McGregor; M.F. Wu; G. Barber; L. Ramanathan; J.M. Siegel “Highly specific role of hypocretin (orexin) neurons: differential activation as a function of diurnal phase, operant reinforcement versus operant avoidance and light level.” [Full Text]
J.M. Siegel “REM sleep” [Full Text]
J.M. Siegel “REM sleep: a biological and psychological paradox.” [Full Text]
M.F. Wu; R. Nienhuis; N. Maidment; H.A. Lam; J.M. Siegel “Role of the hypocretin (orexin) receptor 2 (Hcrt-r2) in the regulation of hypocretin level and cataplexy.” [Full Text]
A. Bhagwandin; N. Gravett; O.I. Lyamin; M.K. Oosthuizen; N.C. Bennett; J.M. Siegel; P.R. Manger “Sleep and wake in rhythmic versus arrhythmic chronotypes of a microphthalmic species of African mole rat (Fukomys mechowii).” [Full Text]
L. Ramanathan; J.M. Siegel “Sleep deprivation under sustained hypoxia protects against oxidative stress.” [Full Text], [Full Text]
J.M. Siegel “Sleep in animals: a state of adaptive inactivity” [Full Text]
2010
J.M. Siegel “Are sleeping pills good for you?” [Full Text]
Y.Y. Lai; T. Kodama; E. Schenkel; J.M. Siegel “Behavioral response and transmitter release during atonia elicited by medial medullary stimulation.” [Full Text]
J.M. Siegel “How much sleep do we actually need?” [Full Text]
R. McGregor; J.M. Siegel “Illuminating the locus coeruleus: control of posture and arousal.” [Full Text]
M.M. Unger; W.H. Oertel; T.C. Thannickal; Y.Y. Lai; J.M. Siegel “Lesions associated with sleep disturbances” [Full Text]
K.A.E. Karlsson; C. Windischberger; F. Gerstl; W. Mayr; J.M. Siegel; E. Moser “Modulation of hypothalamus and amygdalar activation levels with stimulus valence.” [Full Text]
L. Ramanathan; S. Hu; S.A. Frautschy; J.M. Siegel “Short-term total sleep deprivation in the rat increases antioxidant responses in multiple brain regions without impairing spontaneous alternation behavior.” [Full Text]
2009
T.E. Scammell; J.T. Willie; C. Guilleminault; J.M. Siegel “A consensus definition of cataplexy in mouse models of narcolepsy.” [Full Text]
J.P. Pryaslova; O.I. Lyamin; J.M. Siegel; L.M. Mukhametov “Behavioral sleep in the walrus.” [Full Text]
T.C. Thannickal; R. Nienhuis; J.M. Siegel “Localized loss of hypocretin (orexin) cells in narcolepsy without cataplexy.” [Full Text]
J.M. Siegel “Narcolepsy. Interview by Norman Sussman.” [Full Text]
O.V. Shpak; O.I. Liamin; P.R. Manger; J.M. Siegel; L.M. Mukhametov “Rest and activity states in the Commerson’s dolphin (Cephalorhynchus commersonii)” [Full Text]
J.M. Siegel “Sleep viewed as a state of adaptive inactivity.” [Full Text]
J.M. Siegel “The neurobiology of sleep.” [Full Text]
2008
C. Burgess; D. Lai; J. Siegel; J. Peever “An endogenous glutamatergic drive onto somatic motoneurons contributes to the stereotypical pattern of muscle tone across the sleep-wake cycle.” [Full Text]
O.I. Lyamin; P.R. Manger; S.H. Ridgway; L.M. Mukhametov; J.M. Siegel “Cetacean sleep: an unusual form of mammalian sleep.” [Full Text]
J.M. Siegel “Do all animals sleep?” [Full Text]
O.I. Lyamin; J.L. Lapierre; P.O. Kosenko; L.M. Mukhametov; J.M. Siegel “Electroencephalogram asymmetry and spectral power during sleep in the northern fur seal.” [Full Text]
O.I. Lyamin; P.O. Kosenko; J.L. Lapierre; L.M. Mukhametov; J.M. Siegel “Fur seals display a strong drive for bilateral slow-wave sleep while on land.” [Full Text]
J.M. Siegel “Gaps that wake you up.” [Full Text]
T.C. Thannickal; Y.Y. Lai; J.M. Siegel “Hypocretin (orexin) and melanin concentrating hormone loss and the symptoms of Parkinson’s disease.” [Full Text]
Y.Y. Lai; K.C. Hsieh; D. Nguyen; J. Peever; J.M. Siegel “Neurotoxic lesions at the ventral mesopontine junction change sleep time and muscle activity during sleep: an animal model of motor disorders in sleep.” [Full Text]
J. John; L. Ramanathan; J.M. Siegel “Rapid changes in glutamate levels in the posterior hypothalamus across sleep-wake states in freely behaving rats.” [Full Text]
N. Taepavarapruk; P. Taepavarapruk; J. John; Y.Y. Lai; J.M. Siegel; A.G. Phillips; S.A. McErlane; P.J. Soja “State-dependent changes in glutamate, glycine, GABA, and dopamine levels in cat lumbar spinal cord.” [Full Text]
R. Allada; J.M. Siegel “Unearthing the phylogenetic roots of sleep.” [Full Text]
2007
W.P. Hu; J. Da Li; C. Zhang; L. Boehmer; J.M. Siegel; Q.Y. Zhou “Altered circadian and homeostatic sleep regulation in prokineticin 2-deficient mice.” [Full Text]
O. Lyamin; J. Pryaslova; P. Kosenko; J. Siegel “Behavioral aspects of sleep in bottlenose dolphin mothers and their calves.” [Full Text]
J.L. Lapierre; P.O. Kosenko; O.I. Lyamin; T. Kodama; L.M. Mukhametov; J.M. Siegel “Cortical acetylcholine release is lateralized during asymmetrical slow-wave sleep in northern fur seals.” [Full Text]
T.C. Thannickal; Y.Y. Lai; J.M. Siegel “Hypocretin (orexin) cell loss in Parkinson’s disease.” [Full Text]
T.C. Thannickal; J.M. Siegel “Hypocretin Pathology in Human Narcolepsy” [Full Text]
J.M. Siegel “Normal Role of Hypocretin/Orexin” [Full Text]
S.A. Deadwyler; L. Porrino; J.M. Siegel; R.E. Hampson “Systemic and nasal delivery of orexin-A (Hypocretin-1) reduces the effects of sleep deprivation on cognitive performance in nonhuman primates.” [Full Text]
B.Y. Mileykovskiy; L.I. Kiyashchenko; J.M. Siegel “The Activity Profile of Hypocretin Neurons in the Freely Moving Rat” [Full Text]
2006
J. Da Li; W.P. Hu; L. Boehmer; M.Y. Cheng; A.G. Lee; A. Jilek; J.M. Siegel; Q.Y. Zhou “Attenuated circadian rhythms in mice lacking the prokineticin 2 gene.” [Full Text]
J.M. Siegel; L.N. Boehmer “Narcolepsy and the hypocretin system–where motion meets emotion.” [Full Text]
O.I. Lyamin; J. Pryaslova; V. Lance; J.M. Siegel “Sleep behaviour: Sleep in continuously active dolphins; Activity and sleep in dolphins (Reply)” [Full Text]
J.M. Siegel “The stuff dreams are made of: anatomical substrates of REM sleep.” [Full Text]
2005
O. Lyamin; J. Pryaslova; V. Lance; J. Siegel “Animal behaviour: continuous activity in cetaceans after birth.” [Full Text], [Full Text], [Full Text]
B.Y. Mileykovskiy; L.I. Kiyashchenko; J.M. Siegel “Behavioral correlates of activity in identified hypocretin/orexin neurons.” [Full Text], [Full Text]
J.M. Siegel “Clues to the functions of mammalian sleep.” [Full Text], [Full Text]
O.I. Lyamin; J.P. Pryaslova; V. Lance; J.M. Siegel “Continuous activity in cetaceans after birth” [Full Text], [Full Text], [Full Text]
A.M. Blouin; T.C. Thannickal; P.F. Worley; J.M. Baraban; I.M. Reti; J.M. Siegel “Narp immunostaining of human hypocretin (orexin) neurons: loss in narcolepsy.” [Full Text], [Full Text], [Full Text], [Full Text], [Full Text]
J.M. Siegel “REM Sleep” [Full Text]
2004
J. John; M.F. Wu; L.N. Boehmer; J.M. Siegel “Cataplexy-active neurons in the hypothalamus: implications for the role of histamine in sleep and waking behavior.” [Full Text], [Full Text]
J.M. Siegel “Hypocretin (orexin): role in normal behavior and neuropathology.” [Full Text], [Full Text]
J.M. Siegel “The neurotransmitters of sleep” [Full Text]
2003
T. Kodama; Y.Y. Lai; J.M. Siegel “Changes in inhibitory amino acid release linked to pontine-induced atonia: an in vivo microdialysis study.” [Full Text]
T.C. Thannickal; J.M. Siegel; R. Nienhuis; R.Y. Moore “Pattern of hypocretin (orexin) soma and axon loss, and gliosis, in human narcolepsy.” [Full Text]
J.M. Siegel “Why we sleep.” [Full Text]
2002
S. Gulyani; R. Nienhuis; J. John; J.M. Siegel “Cataplexy-related neurons in the amygdala of the narcoleptic dog” [Full Text]
P.R. Manger; H.M. Fahringer; J.D. Pettigrew; J.M. Siegel “The distribution and morphological characteristics of cholinergic cells in the brain of monotremes as revealed by ChAT immunohistochemistry.” [Full Text]
2001
J.M. Siegel; R. Moore; T. Thannickal; R. Nienhuis “A brief history of hypocretin/orexin and narcolepsy.” [Full Text]
J.M. Siegel “The REM sleep-memory consolidation hypothesis.” [Full Text]
2000
T.C. Thannickal; R.Y. Moore; M. Aldrich; R. Albin; M. Cornford; J.M. Siegel “First report of hypocretin (orexin) neuron loss in human narcolepsy: “Human narcolepsy is linked to reduced number, size and synaptic bouton density in hypocretin-2 labeled neurons.”” [Full Text]
J.M. Siegel “Narcolepsy” [Full Text]
J.M. Siegel “Recent developments in narcolepsy research, an explanation for patients and the general public” [Full Text]
T.C. Thannickal; R.Y. Moore; R. Nienhuis; L. Ramanathan; S. Gulyani; M. Aldrich; M. Cornford; J.M. Siegel “Reduced number of hypocretin neurons in human narcolepsy.” [Full Text], [Full Text]
R. A; J.M. Siegel “Sleep and Dreaming” [Full Text]
J. John; M.F. Wu; J.M. Siegel “Systemic administration of hypocretin-1 reduces cataplexy and normalizes sleep and waking durations in narcoleptic dogs.” [Full Text]
1999
Y.Y. Lai; J.R. Clements; X.Y. Wu; T. Shalita; J.P. Wu; J.S. Kuo; J.M. Siegel “Brainstem projections to the ventromedial medulla in cat: retrograde transport horseradish peroxidase and immunohistochemical studies.” [Full Text]
M.F. Wu; S.A. Gulyani; E. Yau; E. Mignot; B. Phan; J.M. Siegel “Locus coeruleus neurons: cessation of activity during cataplexy.” [Full Text]
J.M. Siegel “Narcolepsy: a key role for hypocretins (orexins)” [Full Text]
J.M. Siegel; R. Nienhuis; S. Gulyani; S. Ouyang; M.F. Wu; E. Mignot; R.C. Switzer; G. McMurry; M. Cornford “Neuronal degeneration in canine narcolepsy.” [Full Text]
Y.Y. Lai; T. Shalita; T. Hajnik; J.P. Wu; J.S. Kuo; L.G. Chia; J.M. Siegel “Neurotoxic N-methyl-D-aspartate lesion of the ventral midbrain and mesopontine junction alters sleep-wake organization.” [Full Text]
J.M. Siegel; P.R. Manger; R. Nienhuis; H.M. Fahringer; T. Shalita; J.D. Pettigrew “Sleep in the platypus.” [Full Text]
J.M. Siegel “The evolution of REM sleep” [Full Text]
1998
T. Kodama; Y.Y. Lai; J.M. Siegel “Enhanced glutamate release during REM sleep in the rostromedial medulla as measured by in vivo microdialysis.” [Full Text]
J.M. Siegel; P.R. Manger; R. Nienhuis; H.M. Fahringer; J.D. Pettigrew “Monotremes and the evolution of rapid eye movement sleep.” [Full Text]
M.S. Reid; S. Nishino; M. Tafti; J.M. Siegel; W.C. Dement; E. Mignot “Neuropharmacological characterization of basal forebrain cholinergic stimulated cataplexy in narcoleptic canines.” [Full Text]
J. Kohyama; Y.Y. Lai; J.M. Siegel “Reticulospinal systems mediate atonia with short and long latencies.” [Full Text]
1997
Y.Y. Lai; J.M. Siegel “Brainstem-mediated locomotion and myoclonic jerks. I. Neural substrates.” [Full Text]
Y.Y. Lai; J.M. Siegel “Brainstem-mediated locomotion and myoclonic jerks. II Pharmacological effects.” [Full Text]
D. Nitz; J. Siegel “GABA release in the dorsal raphe nucleus: role in the control of REM sleep.” [Full Text]
D. Nitz; J.M. Siegel “GABA release in the locus coeruleus as a function of sleep/wake state.” [Full Text]
1996
D. Nitz; J.M. Siegel “GABA release in posterior hypothalamus across sleep-wake cycle.” [Full Text]
M.S. Reid; M. Tafti; S. Nishino; R. Sampathkumaran; J.M. Siegel; E. Mignot “Local administration of dopaminergic drugs into the ventral tegmental area modulates cataplexy in the narcoleptic canine.” [Full Text]
J.M. Siegel; P.R. Manger; R. Nienhuis; H.M. Fahringer; J.D. Pettigrew “The echidna Tachyglossus aculeatus combines REM and non-REM aspects in a single sleep state: implications for the evolution of sleep.” [Full Text]
1995
D. Nitz; A. Andersen; H. Fahringer; R. Nienhuis; E. Mignot; J. Siegel “Altered distribution of cholinergic cells in the narcoleptic dog.” [Full Text]
S. Nishino; M. Tafti; M.S. Reid; J. Shelton; J.M. Siegel; W.C. Dement; E. Mignot “Muscle atonia is triggered by cholinergic stimulation of the basal forebrain: implication for the pathophysiology of canine narcolepsy.” [Full Text]
J.M. Siegel “Phylogeny and the function of REM sleep.” [Full Text]
1994
M.S. Reid; M. Tafti; J.N. Geary; S. Nishino; J.M. Siegel; W.C. Dement; E. Mignot “Cholinergic mechanisms in canine narcolepsy–I. Modulation of cataplexy via local drug administration into the pontine reticular formation.” [Full Text]
M.S. Reid; J.M. Siegel; W.C. Dement; E. Mignot “Cholinergic mechanisms in canine narcolepsy–II. Acetylcholine release in the pontine reticular formation is enhanced during cataplexy.” [Full Text]
M.S. Reid; M. Tafti; S. Nishino; J.M. Siegel; W.C. Dement; E. Mignot “Cholinergic regulation of cataplexy in canine narcolepsy in the pontine reticular formation is mediated by M2 muscarinic receptors.” [Full Text]
1993
M.F. Wu; D.J. Jenden; M.D. Fairchild; J.M. Siegel “Cholinergic mechanisms in startle and prepulse inhibition: effects of the false cholinergic precursor N-aminodeanol.” [Full Text]
Y.Y. Lai; J.R. Clements; J.M. Siegel “Glutamatergic and cholinergic projections to the pontine inhibitory area identified with horseradish peroxidase retrograde transport and immunohistochemistry.” [Full Text]
E. Mignot; S. Nishino; L.H. Sharp; J. Arrigoni; J.M. Siegel; M.S. Reid; D.M. Edgar; R.D. Ciaranello; W.C. Dement “Heterozygosity at the canarc-1 locus can confer susceptibility for narcolepsy: induction of cataplexy in heterozygous asymptomatic dogs after administration of a combination of drugs acting on monoaminergic and cholinergic systems.” [Full Text]
1992
J.M. Siegel; R. Nienhuis; H.M. Fahringer; C. Chiu; W.C. Dement; E. Mignot; R. Lufkin “Activity of medial mesopontine units during cataplexy and sleep-waking states in the narcoleptic dog.” [Full Text]
Y.Y. Lai; J.M. Siegel “Corticotropin-releasing factor mediated muscle atonia in pons and medulla.” [Full Text]
T. Kodama; Y.Y. Lai; J.M. Siegel “Enhancement of acetylcholine release during REM sleep in the caudomedial medulla as measured by in vivo microdialysis.” [Full Text]
M.N. Shouse; J.M. Siegel “Pontine regulation of REM sleep components in cats: integrity of the pedunculopontine tegmentum (PPT) is important for phasic events but unnecessary for atonia during REM sleep.” [Full Text]
1991
J.M. Siegel; R. Nienhuis; H.M. Fahringer; R. Paul; P. Shiromani; W.C. Dement; E. Mignot; C. Chiu “Neuronal activity in narcolepsy: identification of cataplexy-related cells in the medial medulla.” [Full Text]
Y.Y. Lai; J.M. Siegel “Pontomedullary glutamate receptors mediating locomotion and muscle tone suppression.” [Full Text]
B.N. Mallick; H.M. Fahringer; M.F. Wu; J.M. Siegel “REM sleep deprivation reduces auditory evoked inhibition of dorsolateral pontine neurons.” [Full Text]
1990
Y.Y. Lai; J.M. Siegel “Cardiovascular and muscle tone changes produced by microinjection of cholinergic and glutamatergic agonists in dorsolateral pons and medial medulla.” [Full Text]
B.N. Mallick; J.M. Siegel; H. Fahringer “Changes in pontine unit activity with REM sleep deprivation.” [Full Text]
P.J. Shiromani; Y.Y. Lai; J.M. Siegel “Descending projections from the dorsolateral pontine tegmentum to the paramedian reticular nucleus of the caudal medulla in the cat.” [Full Text]
M.F. Wu; J.M. Siegel; M.N. Shouse; E. Schenkel “Lesions producing REM sleep without atonia disinhibit the acoustic startle reflex without affecting prepulse inhibition.” [Full Text]
J.M. Siegel “Mechanisms of sleep control.” [Full Text]
Y.Y. Lai; J.M. Siegel “Muscle tone suppression and stepping produced by stimulation of midbrain and rostral pontine reticular formation.” [Full Text]
1989
R. Nienhuis; J.M. Siegel “Analysis of head movement and position using hall effect devices.” [Full Text]
J.M. Siegel; K.S. Tomaszewski; H. Fahringer; G. Cave; T. Kilduff; W.C. Dement “Heart rate and blood pressure changes during sleep-waking cycles and cataplexy in narcoleptic dogs.” [Full Text]
M.F. Wu; B.N. Mallick; J.M. Siegel “Lateral geniculate spikes, muscle atonia and startle response elicited by auditory stimuli as a function of stimulus parameters and arousal state.” [Full Text]
M.N. Shouse; J.M. Siegel; M.F. Wu; R. Szymusiak; A.R. Morrison “Mechanisms of seizure suppression during rapid-eye-movement (REM) sleep in cats.” [Full Text]
E. Schenkel; J.M. Siegel “REM sleep without atonia after lesions of the medial medulla.” [Full Text]
S.S. Suzuki; J.M. Siegel; M.F. Wu “Role of pontomedullary reticular formation neurons in horizontal head movements: an ibotenic acid lesion study in the cat.” [Full Text]
1988
J.M. Siegel; M.A. Rogawski “A function for REM sleep: regulation of noradrenergic receptor sensitivity.” [Full Text]
M.F. Wu; S.S. Suzuki; J.M. Siegel “Anatomical distribution and response patterns of reticular neurons active in relation to acoustic startle.” [Full Text]
Y.Y. Lai; J.M. Siegel “Medullary regions mediating atonia.” [Full Text]
1987
Y.Y. Lai; J.M. Siegel; W.J. Wilson “Effect of blood pressure on medial medulla-induced muscle atonia.” [Full Text]
1986
P.J. Shiromani; J.M. Siegel; K.S. Tomaszewski; D.J. McGinty “Alterations in blood pressure and REM sleep after pontine carbachol microinfusion.” [Full Text]
J.M. Siegel; K.S. Tomaszewski; R. Nienhuis “Behavioral states in the chronic medullary and midpontine cat.” [Full Text]
J.M. Siegel; H. Fahringer; K.S. Tomaszewski; K. Kaitin; T. Kilduff; W.C. Dement “Heart rate and blood pressure changes associated with cataplexy in canine narcolepsy.” [Full Text]
1985
S.S. Suzuki; J.M. Siegel “Reticular formation neurons related to tongue movement in the behaving cat.” [Full Text]
1984
J.M. Siegel; R. Nienhuis; K.S. Tomaszewski “REM sleep signs rostral to chronic transections at the pontomedullary junction.” [Full Text]
1983
J.M. Siegel; K.S. Tomaszewski “Behavioral organization of reticular formation: studies in the unrestrained cat. I. Cells related to axial, limb, eye, and other movements.” [Full Text]
J.M. Siegel; K.S. Tomaszewski; R.L. Wheeler “Behavioral organization of reticular formation: studies in the unrestrained cat. II. Cells related to facial movements.” [Full Text]
J.M. Siegel; R. Nienhuis; K.S. Tomaszewski “Rostral brainstem contributes to medullary inhibition of muscle tone.” [Full Text]
1981
J.M. Siegel; R. Nienhuis; R.L. Wheeler; D.J. McGinty; R.M. Harper “Discharge pattern of reticular formation unit pairs in waking and REM sleep.” [Full Text]
1980
J.M. Siegel; R.L. Wheeler; S.M. Breedlove; D.J. McGinty “Brain stem units related to movements of the pinna.” [Full Text]
1979
J.M. Siegel; R.L. Wheeler; D.J. McGinty “Activity of medullary reticular formation neurons in the unrestrained cat during waking and sleep.” [Full Text]
J.M. Siegel; M.B. Sterman; S. Ross “Automatic detection and operant reinforcement of slow potential shifts.” [Full Text]
J.M. Siegel “Behavioral functions of the reticular formation.” [Full Text]
J.M. Siegel “Behavioral relations of medullary reticular formation cells.” [Full Text]
S.M. Breedlove; D.J. McGinty; J.M. Siegel “Operant conditioning of pontine gigantocellular units.” [Full Text]
J.M. Siegel; S.M. Breedlove; D.J. McGinty “Photographic analysis of relation between unit activity and movement.” [Full Text]
1978
S.S. Bowersox; J.M. Siegel; M.B. Sterman “Effects of restraint on electroencephalographic variables and monomethylhydrazine-induced seizures in the cat.” [Full Text]
J.M. Siegel “Pontine reticular formation neurons and motor activity.” [Full Text]
1977
J.M. Siegel; D.J. McGinty “Pontine reticular formation neurons: relationship of discharge to motor activity.” [Full Text]
J.M. Siegel; D.J. McGinty; S.M. Breedlove “Sleep and waking activity of pontine gigantocellular field neurons.” [Full Text]
1976
J.M. Siegel; D.J. McGinty “Brainstem neurons without spontaneous unit discharge.” [Full Text]
1975
J.M. Siegel “REM sleep predicts subsequent food intake.” [Full Text]
1974
J.M. Siegel “A stereotaxic map of the bony tentorium of the cat.” [Full Text]
1973
J.M. Siegel; P.D. Coleman; A.H. Riesen “Pattern evoked response deficiency in pattern deprived cats.” [Full Text]
1972
H.P. Zeigler; H.L. Green; J. Siegel “Food and water intake and weight regulation in the pigeon.” [Full Text]
People

- Jerry Siegel, Ph.D.
- Oleg Lyamin, Ph.D.
- Ronald McGregor, Ph.D.
- Aftab Alam, Ph.D.
- Cheng Yu-Hsuan, M.S.
- Lalini Ramanathan, Ph.D.
- Ling Shan, Ph.D.
- Joshi John, Ph.D.
- Thomas Thannickal, Ph.D.
- Keng-Tee Chew, M.S.
- K.C. Hsieh, Ph.D.
- Y.Y. Lai, Ph.D.
- Charles Wilson, Ph.D.
- Frank Wu, Ph.D.
Siegel Lab, UCLA Department of Psychiatry
Neurobiology Research 151A3,
VA GLAHS, North Hills
California 91343, U.S.A.
Phone # 818-891-7711
Video and Audio
The discovery of REM sleep
Sleep Research Videos
Sleep Research Audio Tracks
2022 Interview “sleep function, an evolutionary perspective” Lancet Neurology
Alaskan NPR radio interview on whales
Cause of Human Narcolepsy by NPR
Example of Sleep Apnea
The Discovery of REM Sleep
- Aserinsky, E and Kleitman, N. Regularly Occurring Periods of Eye Motility, and Concomitant Phenomena, During Sleep. Science 118, 273-274, 1953
- application/pdf iconAserinsky,E. Memories of famous neuropsychologists: The discovery of REM sleep. J. of the History of the Neurosciences 5, 213-22
- application/pdf iconBrown, C. The stubborn scientist who unraveled a mystery of the night. Smithsonian 92-100, (2003)
- Nathaniel Kleitman Born 1895, Died 1999, Papers at the University of Chicago
- Aserinsky (Born 1921, died 1998) papers at The University of California, Los Angeles 1938-2003
Postpartum Sleep in Whales and Dolphins
Narcolepsy in Dogs
Sleep in Monotremes Platypus and Echidna
- application/pdf iconl., The Echidna Combines REM and Non-REM Aspects in a Single Sleep State: Implications for the Evolution of sleep
- application/pdf iconSiegel, J.M. Sleep in monotremes; implications for the evolution of REM sleep. In Sleep and sleep disorders
- application/pdf iconSiegel, J.M., P. Manger, R. Nienhuis, H.M Fahringer and J. Pettigrew, Monotremes and the evolution of REM sleep. Phil. Trans.
- application/pdf iconSiegel, J.M., Manger, P.R., Nienhuis, R., Fahringer, H.M. and Pettigrew, J.D. Sleep in the platypus. Neuroscience 91: 391-400,
Human sleep deprivation for 17 days: the Science Fair project of Randy Gardner
Useful online resources
About Sleep
About Sleep Disorders
- American Academy of Sleep Medicine – The largest organization of physicians and related professionals devoted to sleep disorders medicine.
- Narcolepsy Network – A national narcolepsy patient support group.
- American Sleep Apnea Association – A national sleep apnea support group.
- The Alberta Lung Association.
- National Heart Lung and Blood Institute – Sleep information for patients and the public
- National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke – Sponsors research on sleep and other neurological disorders
- National Institute of Mental Health – Sponsors research on sleep and mental health health related disorders