Research Laboratory

Leadership
Jerome Siegel, PhD
Director
Contact Info
Sleep Research Website
Neurobiology Research 151A3
VAGLAHS, North Hills, CA
jsiegel@ucla.edu
1-818-891-8612
About
We have been focused on determining the function of sleep, the cause of narcolepsy and the function of the peptide hypocretin (Hcrt or orexin).
We were the first to report the loss of hypothalamic hypocretin neurons in human narcolepsy (in 2000, see below-left, submitted to Society for Neuroscience meeting March 5, 2000 and [PMID:11055430], the first to record hypocretin neurons in behaving animals (in 2005 [PMID:15924864], finding that these neurons fired in relation to approach/pleasurable behavior (click here to see video) and the first to record Hcrt release in the human brain (in 2013 [PMID:23462990]), finding greatly elevated Hcrt release during pleasurable social interactions and minimal release during aversion, disappointment or pain. Neither the activity of Hcrt neurons in rats, nor Hcrt release in humans are strongly correlated with EEG activation or with muscle tone, the two parameters that are altered in narcolepsy. The loss of hypocretin neurons may be responsible for the increased incidence of depression in people with narcolepsy, but the major symptoms of narcolepsy cannot be explained by the loss of these neurons.
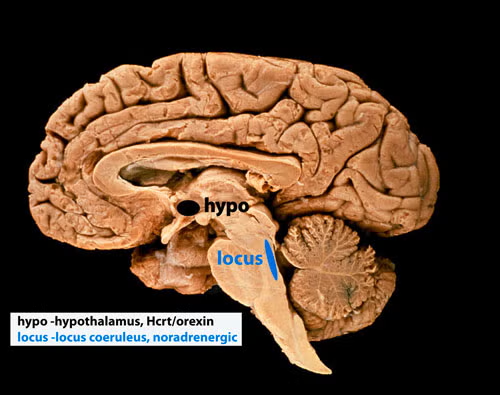
Five to thirty percent of people having narcolepsy with cataplexy have absolutely normal levels of hypocretin in their cerebrospinal fluid [PMID: 10615891]; [PMID: 12374492]; [PMID: 17702265]; [PMID 33539807]; [PMID: 30679597]; [PMID: 26564387]; [PMID: 32406370]; [PMID: 22942503]; [PMID 16006155], findings that do not support the hypothesis that hypocretin loss causes sleepiness and cataplexy, the major symptoms of narcolepsy. In 2025 we discovered that all humans with narcolepsy also have a loss of locus coeruleus noradrenergic neurons (Chi squared p=0.001), comparable in magnitude to their loss of hypocretin neurons [doi.org/10.1101/2025.04.12.648456]. Locus coeruleus neurons facilitate muscle tone and their discharge cessation is correlated with the muscle tone suppression of REM sleep [PMID:10391445]. Thus their loss can explain cataplexy [doi.org/10.1101/2025.04.12.648456]. These noradrenergic neurons also have ascending axons and their loss decreases alertness [PMID:11549748], [PMID:20668280]). Our recent study [doi.org/10.1101/2025.04.12.648456] shows that the loss of locus coeruleus neurons is not caused by the loss of hypocretin neurons.
The two neuronal losses, of hypocretin neurons in the forebrain and of norepinephrine neurons in the brainstem locus coeruleus (see photo below), may be caused simultaneously or sequentially by an autoimmune process [PMID:3010426]. About 150,000 Americans have narcolepsy, a lifelong disorder.
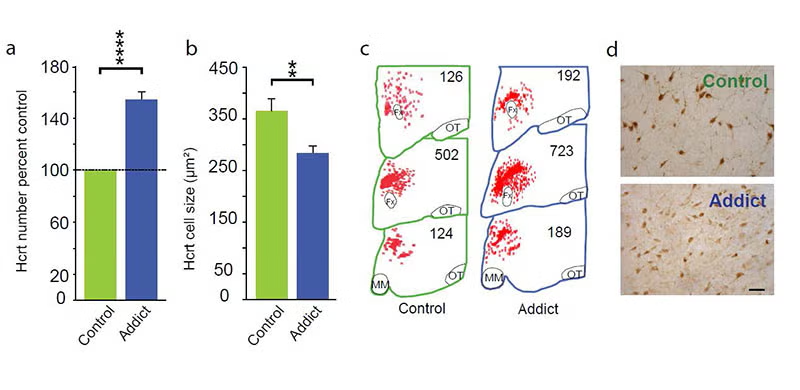
In 2018, 2024 and 2025 (below-left column) we discovered that hypocretin neurons have a major role in opioid addiction. Chronic use of heroin in humans and daily injection of morphine in mice increases the number of detected hypocretin neurons and decreases their size (see figure below). We find that opioid dependence is prevented in mice by deleting hypocretin neurons. In 2024 we found that opioid dependence is prevented, without reducing opioid analgesia, by blocking hypocretin receptors with suvorexant when administering opioids [PMID: 39989723]. About 8 million Americans are dependent on opioids. Opioid dependence caused more than 55,000 opioid overdose deaths last year in the United States. Most individuals who die from an opioid overdose, had their first exposure to opioids prescribed for analgesia.
Bibliography: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/myncbi/jerome.siegel.1/bibliography/public/